
When you stop and start an instance, the public IP address of your instance changes.If your instance is part of an Auto Scaling group, temporarily remove the instance from the Auto Scaling group before starting the resolution steps. Check the instance scale-in protection settings for your Auto Scaling group. Some AWS services use EC2 Auto Scaling to launch instances, such as Amazon EMR, AWS CloudFormation, and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.

VIRTUALBOX UBUNTU KERNEL PANIC SERIAL
For information on configuring the EC2 Serial Console for Linux, see Configure access to the EC2 Serial Console. If your instance is unreachable and you haven't configured access to the serial console, follow the instructions in Method 2: Use a rescue instance. Also, every instance using the serial console must include at least one password-based user. Then, create AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies granting access to your IAM users. You can access the serial console using the Amazon EC2 console or the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI).īefore using the serial console, grant access to it at the account level. The serial console connects to your instance without the need for a working network connection. The serial console helps you troubleshoot boot issues, network configuration, and SSH configuration issues. If you enabled EC2 Serial Console for Windows, then you can use it to troubleshoot supported Nitro-based instance types. Try the SAS or SATA options first, then SCSI, and finally IDE if nothing else works.Use one of the following methods to correct this: You might have to think about which of those controller types existed back in year 2014 when that version of Ubuntu was released: trying NVMe or modern VirtIO options with such an old virtual appliance is probably going to be futile.

There are several virtual hard disk controller options in VirtualBox.
You might have to switch to a different virtual hard disk controller type in VirtualBox settings for this VM. The virtual hard disk controller the VirtualBox provides to the VM is probably currently of a type that is too new, so the virtual Ubuntu 14.04 won't recognize it. If you just added the virtual disk image into a VirtualBox VM configured for a modern version of Ubuntu, no wonder it did not work! Typically, such virtual appliances come with recommended settings for the virtualization software.

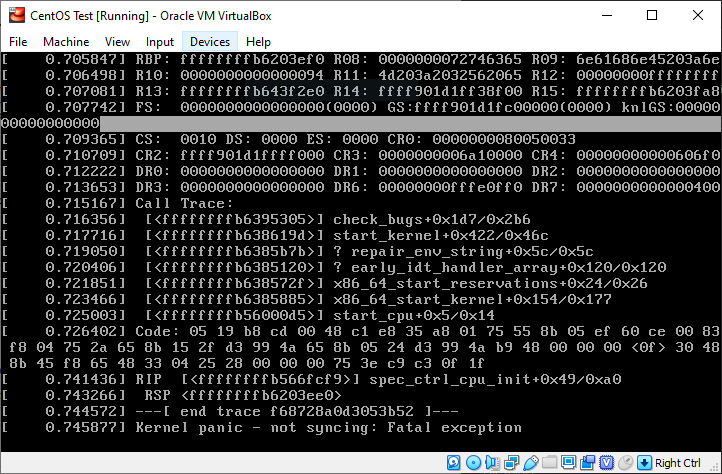
The kernel version 3.13.0-32-generic indicates this virtual appliance is based on a rather old version of Ubuntu: according to this answer on AskUbuntu.SE, this kernel version belonged to Ubuntu 14.04. The message "Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(0,0)" means essentially "I don't even know what kind of disk the root filesystem is supposed to be on." If the end of message said something other than unknown-block(0,0), then it would mean "I found the device that is supposed to contain the root filesystem, but I do not understand the contents, maybe there's something wrong with it?" This is generally what happens when a Linux kernel fails to find a root filesystem.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
